MENU
CLOSE
Digital PLL, All Digital PLL, & Analog PLL:
Which has the Best PPA for Edge AI, IoT, High-performance Cloud, Aerospace…?
Introduction
There are three primary ways of implementing phase-locked loops (PLLs) today: Analog, “Digital” (hybrid), and All digital.
PLLs provide critical clocking functions in today’s chips; when properly customized for a specific SoC, they improve the entire chip’s power, performance, and area — which are critical for nanowatt & multi-gigahertz designs.
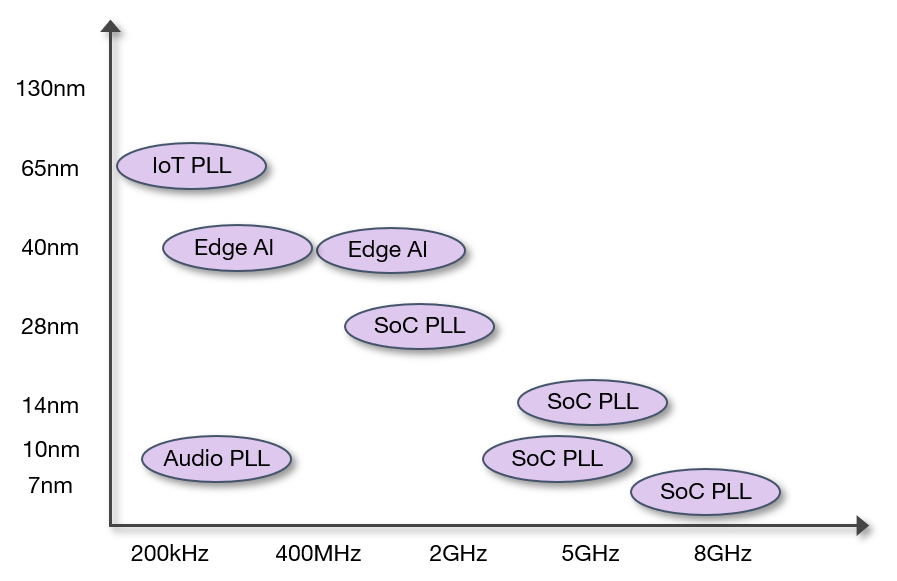
This article reviews some of the varying ability of the three implementation types to scale with process nodes and readily provide optimal PPA for applications such as High-performance Cloud AI, Edge AI, Networking, Processors, IoT, Industrial IoT, Aerospace, Voice control, and Cellular.
Three Major PLL Implementations
Analog PLL
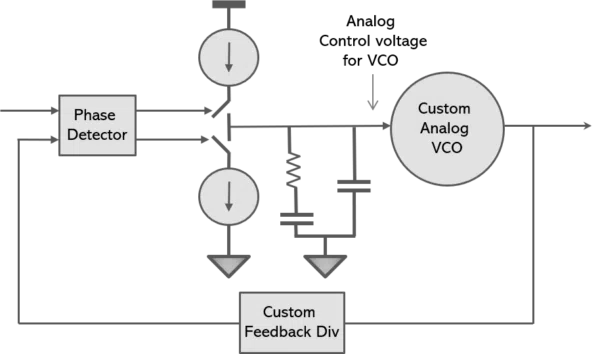
Analog PLL — Contains an analog phase detector, charge pump, loop filter, and voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) in a feedback loop.
Digital PLL
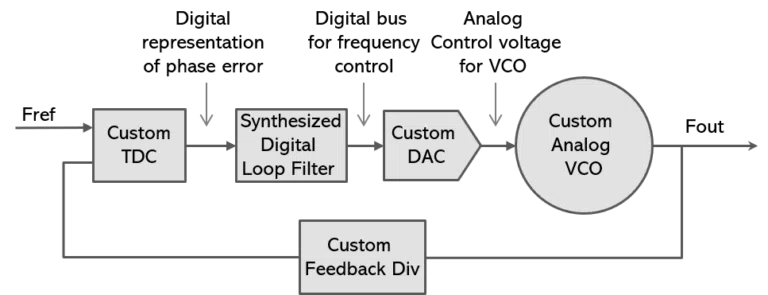
Digital PLL — has a digital phase detector & loop filter, and an analog voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). Digital phase-locked loops are typically smaller than analog PLLs, due to their digital phase detector & loop filter.
All Digital PLL
(Fully Synthesizable)
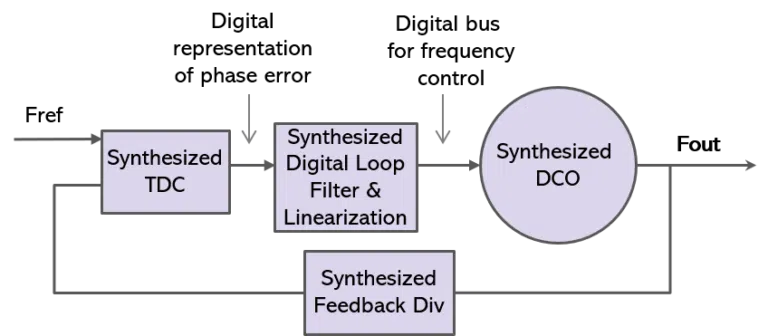
All digital PLL — has all digital elements, including the phase detector, loop filter & oscillator; they do not have the supply voltage limitations of analog PLLs. Advanced all digital phase-locked loops are also fully synthesizable & customizable.
Analog and “Digital” PLLs
A wide range of Analog PLLs is available off-the-shelf. They are also popular for radio front-end applications.
Digital phase-locked loops are typically smaller than analog PLLs, due to their digital phase detector and loop filter.
However, both analog PLLs and digital PLLs contain analog elements. Thus both PLL types:
- Have a stringent lower limit on the supply voltage. The analog circuits require most transistors to remain in the saturation region, and certain low voltage operations, such as near-threshold, may not even be possible with analog for high volume production.
- Are very sensitive to noise in low-voltage operations
- Do not scale well with smaller process nodes
- Have a lengthy development process due to the analog implementation
The result of the lengthy development process is that both Analog PLLs and digital phase-locked loops are both primarily purchased from off-the-shelf product families. Given their availability limits, chip design teams often must:
- Customize their chips for the available IP
- Settle for older process nodes based on IP availability
All Digital PLLs
All digital PLLs do not have the supply voltage limitations of their analog PLL and hybrid analog (“digital PLL”) counterparts. They are also fully synthesizable, so they can be customized and implemented in processes across all foundries, as well as non-standard process nodes in a fraction of the time of analog PLLs.
The resulting key advantages of all digital PLLs are outlined below.
Customizable in Weeks
An all-digital PLL’s master RTL codebase can be configured to generate RTL code that precisely meets customer specifications & application requirements.
Then the completely digital, fully synthesizable architectures enable rapid RTL-to-GDS implementation and optimization — with delivery in weeks.
Wide Voltage & Freq. Range
Can flexibly operate at a wide range of supply voltages, enabling design teams to reduce the power consumption of the entire chip.
Nanowatt Power
Have more flexibility in supporting the lower supply voltage associated with low power designs. This is because all digital circuit architectures do not require precise voltage/current biasing, and therefore are not headroom limited.
Up to 10X Smaller Area
Can be up to 10 times smaller than their analog IP counterparts. This is because they are not dependent on the matching and passive elements required for analog implementations which are a dominant contributor to total area.
Sub-Picosecond Jitter
All digital PLLs inherently have a much higher level of noise immunity than analog and hybrid analog implementations.
Rad-Hardened Designs
Can be radiation-hardened using existing digital libraries, improving overall system performance.
Conclusion
Fully synthesizable, all-digital PLLs offer superior PPA to off-the-shelf analog PLLs and “digital” phase-locked loop IP — including nanowatt power consumption, a wide voltage range, up to 10X smaller area, and low jitter.
They also have a clear time-to-delivery advantage. Fast process porting also allows fast implementation on non-standard process nodes in a fraction of the time of analog PLLs. The fast turnaround time enables late-cycle PDK changes and software-enabled frequency updates to squeeze more performance from the SOC design.
The low-area and fast delivery times give SoC architects the flexibility to use multiple PLLs, each optimized for a particular operating mode.
Movellus Fully-Synthesizable, All Digital PLLs — Customized to Your Application in Weeks
Movellus’ all-digital, application-optimized PLLs are fully synthesizable and can be precisely customized to fit your specific application and targeted process node — in only weeks. Additionally, our fast turnaround time enables late-cycle PDK changes and software-enabled frequency updates to squeeze more performance from the SOC design.
Designers can still use their existing digital implementation tools and methodologies for static timing analysis, synthesis, place and route, and design for testability (DFT).
We support processes from all foundries, including TSMC, Samsung, GlobalFoundries, UMC, Fujitsu, etc…
Low Power & Ultra-Low Power PLLs
- Movellus’ architecture allows us to create nano-watt customized PLLs that are orders of magnitude smaller than traditional analog PLLs.
- Output Frequencies: 10 kHz to 1 GHz
- Power: 700 nW to 100+ uW
- We can satisfy the most demanding requirements for low-power designs, even battery-less applications for markets such as Edge AI and IoT.
High-Performance PLLs
- Movellus’ architecture allows us to create multi-GHz customized PLLs orders of magnitude smaller than traditional analog PLLs.
- Output Frequency: 100 MHz to 10 GHz
- Core PLL Power: < 1.2 mW/GHz
- Our high-performance PLLs have a wide frequency and voltage range — enabling dynamic voltage & frequency scaling (DVFS) for SoCs.
- We can maintain key PLL performance metrics over a wide range of input & output frequencies, enabling architecture tradeoffs not traditionally available.
- Applications for Movellus’ high-performance PLL IP blocks range from complex SOC clocking to high-speed SERDES while maintaining simplicity & ease-of-use.
Stay Connected
Stay Connected
By clicking “Accept”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. ACCEPTREJECT
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __hssrc | session | This cookie is set by Hubspot whenever it changes the session cookie. The __hssrc cookie set to 1 indicates that the user has restarted the browser, and if the cookie does not exist, it is assumed to be a new session. |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| JSESSIONID | session | The JSESSIONID cookie is used by New Relic to store a session identifier so that New Relic can monitor session counts for an application. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __hssc | session | HubSpot sets this cookie to keep track of sessions and to determine if HubSpot should increment the session number and timestamps in the __hstc cookie. |
| __hstc | session | This is the main cookie set by Hubspot, for tracking visitors. It contains the domain, initial timestamp (first visit), last timestamp (last visit), current timestamp (this visit), and session number (increments for each subsequent session). |
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _ga_F75FB76KBW | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. |
| _gat_gtag_UA_60322432_1 | 1 minute | Set by Google to distinguish users. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| hubspotutk | session | HubSpot sets this cookie to keep track of the visitors to the website. This cookie is passed to HubSpot on form submission and used when deduplicating contacts. |